Mosquitoes
Mosquitoes may be not be classed as pests but their presence may cause a nuisance. Even in the absence of disease transmission, mosquito bites can result in allergic reactions, producing significant discomfort and itching. The Isle of Wight Council does not provide a pest control service. However, if you consider that you require assistance you may wish to contact one of the Isle of Wight Council Approved Pest Control Contractors.
Click here for a list of the Council’s Approved Pest Control Contractors
If in doubt telephone your local Environmental Health Department.
Tel: 01983 823000.
Identification:
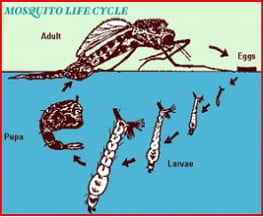
Life Cycle.
Mosquitoes may survive winter as eggs, fertilized adult females or larvae. Eggs, larvae and pupae must have water to develop.
Female mosquitoes lay their eggs directly on the water surface.
Larvae feed on bits of organic matter dispersed in the water, becoming full grown in about one week.
The pupal stage lasts two to three days.
Female mosquitoes are ready to bite one or two days after adult emergence.
Male mosquitoes do not bite but feed on flower nectar or plant juices.
Adults may fly 5 to 10 miles, but usually rest in grass, shrubbery or other foliage close to the water breeding area.
Mosquitoes may transmit diseases to humans.
PREVENTION.
Since most mosquitoes may not travel very far, the risk of spreading can be minimized by controlling the mosquito breeding sites which are in close proximity to your home. Water management, to prevent mosquito breeding, is essential for control. Eggs do not hatch unless they are in water. Remove old tyres, buckets, tin cans, glass jars broken toys and other water catching devices. Change water in bird baths and wading pools once or twice a week; clean out roof gutters holding standing water; place tight covers over cisterns, cesspools, septic tanks, barrels and tubs where water is stored. Fill, drain or treat tree holes; and drain or fill stagnant water pools, puddles, ditches or swampy areas. Stock ponds and reservoirs with fish.
Repellents applied to the skin and clothing will prevent mosquito bites for one to five hours depending on the person, type, and number of mosquitoes and the type and percent of active ingredient in the repellent. Repellents are available as aerosol sprays, pump sprays, creamsticks, lotions or foams.
Repellents applied to the skin and clothing will prevent mosquito bites for one to five hours depending on the person, type, and number of mosquitoes and the type and percent of active ingredient in the repellent. Repellents are available as aerosol sprays, pump sprays, creamsticks, lotions or foams.
For more information regarding this Leaflet
Please contact:
Environmental Health Service
Jubilee Stores
The Quay
Newport
Isle of Wight
PO30 2EH
Telephone: 01983 823000
Facsimile: 01983 529804
©Isle of Wight Council, May 2004
©Isle of Wight Council, May 2004
Page last updated on: 30/08/2007





