Appendix 7 -

DEVELOPMENT PLAN
INTRODUCTION
The tourism industry has been asked to contribute towards a number of strategic planning processes including the Community Plan – Island Futures. The Tourism Partnership Limited is committed to a planning initiative “Tourism Development Plan” (TDP) which seeks to shape the way the Island manages itself to take full advantage of economic, environmental and community opportunities. It will map out a future for the Island’s main industry over the next 10-15 years whilst contributing to Island Futures and other programmes.
Being an island undoubtedly
presents advantages and opportunities for tourism and has given the Isle of
Wight some very distinctive characteristics, both positive and negative. Peripherality (being cut off from mainland
UK) has led to relative under-development - this has preserved a superior
environment but can also inhibit economic activity. In the same way, being an
attractive retirement destination has resulted in a higher than average aged
population. The latter is exaggerated by a failure to make the Isle of Wight
attractive for young people to live and work in comparison to many other parts
of the UK.
There is clearly a need to
stimulate a stronger mixed economy whilst retaining the Island’s unique
bio-diversity and quality of life. “Wise tourism” development should also aim
to ensure economic benefits are not made at a cost to the social fabric or the
environment. Wherever possible it should deliver real benefits to all. A SWOT (strengths,
weaknesses, opportunities & threats) analysis has been included which
identifies many of the issues facing the Island’s tourism industry.
Isle of Wight Tourism’s existing plan “Strategy 2001” looks forward to the next three years 2001 to 2003. It attempts to identify important issues and prioritise action to maximise opportunities and develop solutions to challenges. It looks at the following:
à Explains why tourism is important to the Island and what role tourism can play
à Discusses the challenges and opportunities tourism brings
à Identifies strategic objectives for Isle of Wight Tourism
When finalised the TDP will provide a
framework for business planning and investment whilst ensuring community and
environmental priorities are achieved. Isle of Wight Tourism Strategy
will be reviewed annually and will be developed and implemented to support the
Tourism Development Plan. Departmental business plans within IWT will ensure
that available resources are focussed on achieving strategic objectives with
clear performance indicators that are properly benchmarked. The TDP will
complete a process of “creating the right framework to get things done” which
was the first priority set by Government for the tourism industry.
LEADING THE PLANNING PROCESS
It is important that the TDP process has clear leadership in which the industry and other stakeholders can be confident. A lead group (LG) has been formed to start this process. The LG should demonstrate a range of ability and experience with the potential to deliver clear direction which is both visionary and innovative whilst remaining practical and achievable.
Initially the LG will consist of the following:
Peter Moore OBE (Chairman) Chairman ETC Resort Regeneration Task Force
Simon Dabell Chairman Island Tourist Industry Association (ITIA)
Tim Addison Head of Tourism Services, IWC
Cllr Peggy Jarman Executive spokesperson for Leisure & Tourism, IWC
Nicky Hayward MBE ETC Tourism Cabinet, SEEDA Tourism Sector Group
Peter Colling Head of Research and Development, Southern Tourist Board
John Bentley Policy Director, Isle of Wight Partnership
Peter Tuck Chairman Quality Transport Partnership
Adam Hill Director, Designate (IWT Advertising Agency)
Annie Horne Managing Director, Wight Leisure
Paul Airey Head of Planning Policy
Additional representatives from tourism business sectors will be involved at all stages and co-ordinated with the ITIA Executive. The group will meet first in September 2001 and thereafter monthly for the first three months.
WHERE ARE WE NOW?
Initial phase of the TDP will establish a context for the plan. The plan will be progressed as follows:
August 2001 Produce a baseline report on Sandown Bay IWT
September 2001 First Lead Group meeting IWT
Report to Tourism Partnership IWT
Review baseline statement LG
Island perceptions brief agreed LG
Market research brief agreed LG
October 2001 Draft TDP framework LG
Consultation brief LG
November 2001 Draft TDP to Tourism Partnership IWT
December 2001 Revised draft delivered for Community Plan IWT
As a starting point the remainder of this document aims to set out a short summary of factors and issues which are well known and accepted by most Island agencies. These identify areas for consideration by the TDP and state some assumptions about tourism in general and tourism on the Isle of Wight. These will all be reviewed and amended where necessary through the TDP process.
Two appendices have been attached which have been taken from the IWT Strategy 2001, these cover existing partnership arrangements (Appendix 1) and the economic impact of tourism (Appendix 2).
WHAT IS MEANT BY TOURISM?
Tourism has been a part of Island
life for more than 200 years, since the late 1700s. “ Resorts began to be
developed in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries and, in the main,
flourished well into the twentieth century. They were able to capitalise on
changes in society, such as the growing amount of leisure time, increasing
discretionary income and greater mobility, provided first by the railways and
then the car. In the 1970’s, however,
the situation began to change. Packaged
holidays to overseas destinations with a more reliable climate, followed by
cheaper air travel and a growth in the number of domestic destinations meant
that resorts faced increasing competition both at home and abroad.” –
English Tourism Council “Sea Changes” February 2001
The definition of tourism is quite
broad and embraces all visitors to the Isle of Wight, whether they are from the
mainland or overseas. It includes
anyone who is staying overnight, on holiday, for business purposes or visiting
friends and relatives. It also includes
people visiting the Island on day trips, primarily for leisure purposes as
opposed to education and work.
Which businesses are in the
tourism industry? This question is still being debated but there is a consensus
now that accepts that business sectors such as retail are often as dependent on
visitor income as a hotel. On the IW, the links are reasonably clear to most
residents but the economists often stick with more traditional methods, listing
retail as a distribution business. The recent Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD)
crisis (February to June 2001) did much to demonstrate the interdependence of
tourism and other business in rural economies.
Sustainable tourism also requires a definition. As tourism effects the environment and the people who live in destinations the industry should be managed in a responsible way. IWT is committed to the principles of sustainability and all of its programmes consider impacts beyond economic benefits. Sustainable Tourism has been defined as “tourism which meets the needs of Islanders and visitors while protecting and enhancing opportunities for the future”. It is about finding the right relationship between visitor, place and community.
WHAT ARE THE
BENEFITS OF TOURISM?
“Tourism is a powerhouse,
worth around £64 billion to the UK economy each year, 6% of the gross domestic
product. It employs 7% of the UK workforce (nearly 2 million people) and
creates up to one in four of all new jobs.”
England’s Regional Tourist Boards “Agenda for Tourism” May 2001
Tourism is
recognised to benefit the Isle of Wight in the following ways:
à
Boosting
the economy
Tourism
works like an export industry attracting additional money into the local
economy. Tourism can also play a useful
role in diversifying the economy of rural areas and regenerating towns.
à
Generating
employment
Visitor
spending supports and creates jobs spread throughout the economy. One in four
of all jobs on the Island depend on tourism.
à
Creating
a positive image
Tourism
is always associated with positive images.
Tourism can help raise the awareness of places, change perceptions,
create interest and encourage inward investment and civic pride. A place that people want to visit is usually
a good place in which to live and work.
à
Sustaining
local facilities
Visitors
can help support facilities which local people use, resulting in greater
variety and a higher quality of provision.
This can apply to theatres, galleries, restaurants, shops, museums,
visitor attractions and public transport.
A thriving tourism industry can help improve the quality of life for a
local area.
à
Supporting
a better environment
Tourism
thrives in attractive environments.
Visitor related issues can provide new life for historic buildings and
tourism developments have provided the catalyst for regeneration often
highlighting the importance of local biodiversity (animals, plants, insects…).
ISLE OF WIGHT TOURISM PRODUCT
The Island is a distinctive destination that combines rural countryside, diverse coastline with traditional seaside resorts, towns and villages. Its very diversity makes the tourism product difficult to categorise. Once known as “Little England”, the Isle of Wight must re-establish relevant brand values for today’s market place building on strengths: world reputation of Cowes Week regatta, quality environment highly suitable for walking, cycling and sailing, peace and tranquillity, ease of access, quality accommodation and of course Island status. Here some of these issues are explored further:
Accessibility
The Solent, a three-mile stretch of water that separates the Island from the mainland, has positive implications for tourism – it makes our destination distinctive. The ferry crossing creates a sense of “getting away”, and underlines all that is special about visiting an island. However, concerns over journey times, ease of travel connections and cost have certainly curtailed growth in short break markets. In fact cross-Solent operators provide three car ferry routes (Portsmouth to Fishbourne, Southampton to Cowes, and Lymington to Yarmouth), passenger-only high-speed services between Southampton and Cowes, Portsmouth and Ryde with the world’s last scheduled passenger hovercraft between Ryde and Southsea (Portsmouth).
The Island is easy to reach via the M3, A3 and M27. Portsmouth and Southampton are the key ports of entry and in addition to accessibility by road, are served by key rail routes. The continental ferry port at Portsmouth serves as a gateway to Europe and many overseas visitors pass through. Heathrow and Gatwick, along with the less active but closer Bournemouth, Southampton and Eastleigh airports, are within easy reach.
Overall rather than being less convenient for shorter breaks the Island is much closer to markets in London, south east and midlands than many of its rival UK destinations (Cornwall, Devon, Channel Islands, Cotswolds…)
Main towns and resorts
In recent years high street names have moved to the Island, with the Island’s capital Newport now being accepted as the main retail centre. A multiplex cinema opened in Newport in 2000 that significantly added to the town’s leisure facilities. The future of Newport’s market is the subject of much discussion over its content and location.
Sandown, Shanklin, Ventnor and Ryde represent the Isle of Wight’s most established tourism areas. All benefit from excellent beaches that are a major tourism and recreational resource and there is a concentration of accommodation establishments and related infrastructure in these areas. It is important to differentiate Island resorts from their much larger and more developed mainland counterparts (Bournemouth, Torbay, Margate…). However all resort towns on the IW are in need of significant regeneration:
“The decline in resorts has
been slow and subtle and, therefore, difficult to detect. Nonetheless, the overall result of changes
over the last 30 years has seen the share of domestic holidays taken at the
seaside decline dramatically. The
seriousness of this decline should not be underestimated. If no action is taken, the decline in some
resorts will be terminal. Inactivity
will also have a wider social cost. The
Government has recently announced substantial funding for the renewal of our
most deprived neighbourhoods.
Continuing decline will, for many of our resorts, result in them
becoming the major regeneration problems of tomorrow, with the attendant costs
and social implications that that entails.”
– English Tourism Council
“Sea Changes” February 2001
Ryde is an important gateway town and the current SRB VI regeneration programme will seek to revitalise its tourism role, Ventnor has an established regeneration scheme which is on-going with significant results achieved.
Sandown Bay (Sandown, Yaverland, Lake and Shanklin) must be the next priority area for regeneration. Sandown and Shanklin have now both been included into the Rural Development Area and together with Ventnor should be considered as coastal villages.
Countryside and Coastal areas
The countryside and rural areas of the Island are largely designated as Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty. These areas now support a wide range of accommodation establishments, places of interest and visitor attractions. In addition, walking and cycling are popular with visitors and these are supported, encouraged and promoted through events, such as the IW Walking Festival now the largest of its kind in the UK . Rural economies can often no longer rely on farming as a sole revenue source and must look to diversify. Tourism offers a complementary income stream for many rural businesses and the Island can boast many examples of best practice in this area.
The Isle of Wight is surrounded by some of the most beautiful and dramatic coastline in Europe, from safe sandy beaches in resort areas to the famous coloured sands of Alum Bay and The Needles rocks. Much of the coastline is environmentally protected and unspoilt, supporting a huge range of animal, bird and plant life – many species unique to the Island. The coastal waters are well known to yachtsmen around the world and are the home to the sailing world’s most famous regatta – Cowes Week.
Cowes and Yarmouth are well known for their sailing connections and as cruising bases, whilst there is increasing interest in water activities such as windsurfing and surfboarding.
The recent FMD crisis demonstrated the growing dependence of rural economies upon diversification into leisure and tourism and so the importance of tourism in future rural strategies.
“Tourism income is fundamental for the rural economy
and has played a central role in revitalising many small towns and their
surrounding areas and there is considerable potential for further growth.”
- Department of the Environment, Transport and the Regions “Our
Countryside: The Future
A Fair Deal for Rural England”
Visitor Attractions and Places of Interest
The Island has perhaps more recognised attractions
per square mile than any other destination in the UK although few are able to
attract visitors to the Island in their own right. Undoubtedly a key factor in
many visitors returning year after year is the wealth of things to see and do,
which are not intrusive to the character of the Island and which range from
significant historic properties through to modern family facilities.
Much of the Island’s heritage can
be attributed to its close associations with the Royal family primarily Charles
1 (Carisbrooke Castle) and Queen Victoria (Osborne House). The Royal patronage
made the IW one of the most fashionable destinations in the world during the
Victorian era. Many famous Victorian people then made the Island their home,
including the poet Alfred Lord Tennyson, adding to its cachet.
Accommodation
The IW remains the UK’s only major
destination to be 100% committed to exclusively promoting graded and inspected
accommodation - indeed in the UK only around 50% of all accommodation is graded
and inspected. This represents an important commitment to quality and has
certainly ensured that minimum standards on the island exceed those in similar
mainland areas.
Accommodation is also varied, with
traditional seaside hotels and guesthouses as well as some of the most
attractive holiday parks and caravan/camping sites in the SE England. The Farm
accommodation sector is growing with self-catering establishments of all styles
signalling a growth in demand for this type of facility.
However, like the resorts
themselves, the Island’s existing accommodation must continue to meet the high
expectations of today’s visitor. This is an incremental process, which should
be led by a programme of regeneration throughout the island.
ISSUES AFFECTING TOURISM ON THE ISLE OF WIGHT
One simple way to examine various issues is to undertake a SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats) Analysis. This lists down factors that need change, some of which can be influenced easily and some which are almost impossible, as well as describing those factors that need to be retained and protected. The following is a SWOT analysis for the Island product compiled by team members of IWT:
Strengths
1. Island -
feeling of “getting away”
2. Good rail
and road connections to ports of entry
3. Close to ingress
point for continental ferry
4. Safe,
attractive environment
5. Promoted
accommodation 100% graded and inspected
6. Safe,
clean family beaches
7. Sunshine
hours vs mainland
8. Spectacular
coastal and inland terrain - AONB, biodiversity
9. Relative
under-development
10. Pace of
life
11. World
centre for yachting activity
12. Some high
quality visitor attractions and places of interest
13. Historic
buildings – Carisbrooke Castle, Osborne House, Roman Villa
14. Culture
& heritage - Royalty and historic figures
15. Wide range
of accommodation to suit all styles and budgets
16. Quality of
Island pubs
17. Diversity
of towns and villages (Ryde vs Calbourne….)
18. Effectiveness
of low budget campaigns
19. Visitor
attractions – historic, cultural, play & modern
20. Variety of
outdoor activities – walking, cycling & sailing
21. Events
programme – Cowes Week, Walking Festival….
Weaknesses
1. Under-investment
in infrastructure – “civic pride”
2. Many
agency services are designed for a “mainland economy” (5% tourism)
3. Strategic
importance of tourism in Island agencies
4. Non-integration
of public transport
5. Island
roads have capacity issues - overcrowding, parking
6. Perceived
cost and hassle of getting to the Island
7. Resorts in
need of regeneration and investment
8. Diversity
of product difficult to promote
9. Seasonality
of traditional business
10. Planning
constraints vs appropriate tourism development
11. Under-supply
of higher demand products – eg rural self catering
12. Public
transport expensive and lacks coverage in some areas
13. Limited
indoor attractions for wet weather (? – needs definition)
14. Lack of
consistency in quality of attractions and places of interest
15. Failure to
enforce building improvement notices in sensitive areas
16. Lack of
professionalism in leisure/tourism/hospitality
17. No sense
of understanding core product
18. Community
planning lacks direction and co-ordination
19. Lack of
competition – “Island Standards” apply
20. Image -
bucket & spade, elderly..
21. Lack of
quality places to eat/entertainment (? – needs definition)
Opportunities
1. Tourism is
a growth industry – UK short breaks
2. Reduced
seasonal sensitivity in new short break markets
3. Improved
access to information and distribution – on a global basis
4. Improving
skills base in tourism/hospitality
5. IW
recognized as a Rural Development Area (funding)
6. SRB6 –
town regeneration programme in Ryde
7. Tourism
can demonstrate benefit to “quality of life” for residents
8. E-commerce
opportunities – industry very suitable for development
9. Profitable
partnerships – ETC, STB…
10. Introduction
of better quality standards (attractions etc)
11. Improvements
in non-tourism sectors
12. Sustainability
of tourism on Island – green industry
13. Potential
to improve IW College
14. Lifestyle-led
tourism, suits Island product –Walking, Cycling & Sailing…
15. Government
emphasis on environmental issues – transport improvements
16. Potential
for car-free tourism
17. Develop
centre of excellence for quality of life (organic farming..)
18. Overseas
visitor markets
19. Corporate
and incentive travel
Threats
1. Under
valuation of tourism by the Island
2. UK main
season holiday market in serious decline
3. Macro-economic
issues (recession)
4. Currency
fluctuations
5. Competition
- low cost and easy availability of overseas holidays
6. Competition
- domestic
7. Loss of
accommodation capacity to residential/other uses
8. IW could
lose its “difference” and become more like the Mainland
9. Conservation
will inhibit leisure developments in line with consumer expectations
10. Lack of
continuity in local Government planning and finance
11. Island
residents don’t appreciate relevance of tourism
12. New
customer expectations may out pace Island ability to improve product
13. Lack of marketing
budget allowing competitor destination advantage
14. Growing
interest in UK city breaks
15. Fuel costs
– ferry prices could rise
IWT and its partners can work together to tackle many of the above
challenges (illustrated in the objectives set out below). However there will be
significant gaps that should be addressed by the Tourism Development Plan to
direct IWT, its partners and other agencies in the future.
CHALLENGES FOR THE FUTURE
A tourism development plan for the Isle of Wight must look at specific issues affecting the county and also take account of the wider context in which tourism must operate. It addresses the economic issues, but also those which concern Island residents and the environment.
The Government’s Tourism Strategy for England is set out in “Tomorrow’s Tourism” published by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport in 1999, whilst a regional context is set out in the Regional Tourism Strategy published by the Southern Tourist Board in the same year. Both these documents identify the potential for growth and highlight the importance of local authorities in helping to deliver tourism objectives.
Key themes from these
strategies are;
à
Improving the quality of the product and becoming
more customer focused
à
Improving the delivery and co-ordination of
marketing
à
Exploiting Information Technology in delivering
services/improving marketing intelligence
à
Sustainable development protecting the environment
and respecting local communities
à
Developing the skills of the local workforce and improving
tourism jobs
à
Improving access to tourism for all sectors of the
community
à Improving the image of the industry
Tomorrow’s Tourism has provided the strategic framework upon which the TDP and Isle of Wight Tourism’s strategy and business plan have been developed.
FINALLY
Finally, IWT will co-ordinate the production of a Tourism Development Plan. This will be linked to the IWC Community Plan – Island Futures (Local Strategic Plan) and IWP Regeneration and set out how tourism infrastructure on the Island should be developed over the next 15 years. The Tourism Partnership Limited will act as sponsor for the TDP and review its progress at regular intervals. It is hoped that it will also influence Government support for tourism on the Isle of Wight at a national and most importantly at a regional level.
Tim Addison
Head of Tourism Services
Isle of Wight Tourism
June 2001
Appendix 1
PARTNERSHIP
Isle of Wight Tourism is a
partnership between the Isle of Wight Council and the Island Tourist Industry
Association (ITIA) that represents more than 850 Island businesses. In addition
IWT works with a number of key organisations both on and off-Island, these
include:
Sustainable Tourism Forum Southern Tourist
Board English Tourism
Council
British Tourist Authority Isle of
Wight Partnership
British Resorts Association South
East England Development Agency
KEY PARTNERS IN TOURISM ON ISLE OF WIGHT
ISLE OF WIGHT COUNCIL (IWC)
MISSION STATEMENT - “To Improve Island Life”
IWC’s Tourism Services department
has been placed within the Executive Services directorate. Its headquarters are
at the Westridge Centre, Ryde with seven tourist information centres based in
Cowes, Newport, Ryde, Sandown, Shanklin, Ventnor and Yarmouth.
ISLAND TOURIST INDUSTRY ASSOCIATION (ITIA)
MISSION STATEMENT - Supporting Isle of Wight
Tourism to promote the Island as a leading, quality tourist destination in
partnership with the Isle of Wight Council.
An independent business association originally created from a number of smaller independent associations to work with the IWC. The ITIA executive consists of the individual association chairmen, it also nominates representatives to serve as board directors to the Tourism Partnership Limited (TPL).
ISLE OF WIGHT TOURISM (IWT)
MISSION
STATEMENT - As part of the Isle of Wight Council and working in partnership
with the Island’s tourism industry, Isle of Wight Tourism aims to promote the
Isle of Wight as one of the UK’s leading, quality tourist destinations.
The umbrella brand under which IWC Tourism Services works with ITIA to present a cohesive and easily recognised local tourist board to support business on the Isle of Wight. This arrangement is subject to a formal agreement which is reviewed yearly and renewed every three years by the Head of Tourism Services and Chairman of ITIA.
TOURISM PARTNERSHIP LIMITED
(TPL)
A key priority for the coming year
will be to re-energise the Tourism Partnership Limited. This board of 12
directors consists equally of persons nominated by Isle of Wight Council and
ITIA and was originally formed to oversee the externalised tourism service that
existed in the early 1990s. Since services were amalgamated under the control
of IWC in 1997 the TPL has seen its terms of reference change. Now that the IWC’s
modernised agenda and new council model has been established it is
perhaps the right time to examine this Board as the bridge between the tourism
industry, the IWC and other important agencies.
Appendix 2
ECONOMIC IMPACT OF TOURISM TO THE ISLE OF WIGHT
The Isle of Wight has one of the
highest rates of unemployment in the south east of England. Traditional
manufacturing and agriculture have declined across the UK and the Island has
not been immune. It has also failed to replace these industries as well as in
other parts of the country.
During February 2001, 6.3%
of the Island’s working population was out of work making the IW second only to
Thanet in the league of areas of highest unemployment in the SE England. Unemployment
Headlines February 2001 – IW Partnership
Tourism has subsequently become
increasingly important with 1:4 Island jobs wholly and partly dependent on
visitor income. This constitutes between 30-40% of our economy measured as
Gross Domestic Product (GDP). However these figures vary considerably and there
is a clear need to better understand the financial impact which tourism in the
21st century has on the Isle of Wight.
IWT undertakes a quarterly survey
of tourism activity. The following information is taken from the 1999/2000 full
year survey:
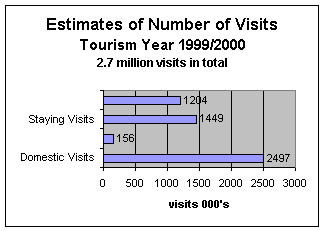
Across the whole year there were
2.7 million visits to IW
Tourism occurs throughout the year
with an average of 34,000 per week at the lowest point to 1000,000 per week
during the peak season
1.5 million were staying visits
requiring 6.7 million bednights
Key points in the year include:
Holiday/leisure stays reached 890,000 in the year.
Short stay holidays (1-4 nights) were more common than longer stay holidays
(5+nights): 526,000 versus 364,000. The majority of holiday trips were
described as an ‘other holiday or leisure stay’ showing that the Island is
succeeding in attracting short breaks and additional holidays. Only 104,000
holidays were described as a ‘main holiday’.
There were 348,000 staying visits to see
friend/relatives and around 182,000 day visits to see friend/relatives, a total
of over half a million trips.
Business visits were most likely to be day trips
(417,000 visits). Staying business visits (including business combined with
leisure trips) reached 155,000 visits. Approximately a quarter of all business
visits arose from tourism, retailing and catering business.
Annual bed occupancy in catered accommodation was
47% but ranged from 15% in January to 82% in August;
Annual room occupancy in catered accommodation was
56%; this ranged from 18% in January to 88% in August;
Average length of stay across all domestic visits was 4.4 nights but this ranged from 2.9 in Q2 to 6.1 in Q4.